ABOUT CANCER
SGS Cancer Hospital offers direct treatment through innovative, evidence-based treatments that comply with the highest safety and transparency requirements, with patient needs always taking priority. Our staff provides ongoing collaboration regardless of the stage or kind of tumor. Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that has proven to be particularly effective in the treatment of sickness. We provide therapeutic services in addition to chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Anal Cancer
Anal cancer is a malignant tumor of the anal canal or anal verge, the gastrointestinal tract’s edge. It often spreads by direct invasion into surrounding tissue or via the lymphatic system. Although it is uncommon, anal cancer can spread through the blood.
“Malignancies of the anal verge account for 25% of all anal cancers.”
Anal malignancies can be caused by a variety of circumstances, and they occur when normal, healthy cells become abnormal due to a genetic mutation. Cells reproduce at a set pace under normal conditions, and they also perish at a specific rate.
When it comes to aberrant malignant cells, they grow quickly and, more importantly, they do not die. That is, they ultimately grow out of control and begin to accumulate, resulting in the creation of a tumor. If left untreated, these malignant cells can spread to distant organs and disrupt the body’s regular functioning.
Throat cancer
Cancerous tumors that grow in the Nasopharynx (upper portion of the throat, behind the nose), Oropharynx (middle part of the throat), Hypopharynx (bottom part of the neck), and larynx are referred to as throat cancer (voice box).
Throat cancer lesions are often seen in a person’s throat, voice box, or tonsils. The throat, also known as the pharynx, is a 5-inch-long tube that goes from the nose to the neck.
The tonsils are two lumps of soft tissue at the back of the throat. The voice box, also known as the larynx, is the region of the respiratory system that contains the vocal cords and produces vocal sounds.
Advanced throat cancer may spread to all three of these areas, as well as surrounding lymph nodes, blood vessels, and organs.
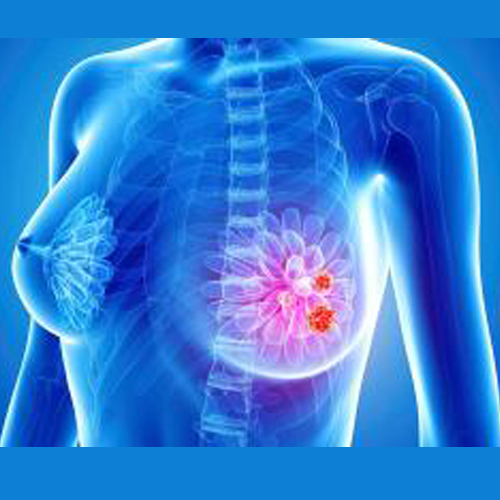
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the breast tissues. It is one of the most frequent malignancies in women worldwide. A woman’s odds of being diagnosed with the condition at some point in her life are one in eight. As a result, it is critical for women to be informed about breast cancer and its treatment.
- An alteration in the size or form of one or both breasts
- Skin redness or rash around the nipples
- Nipple discharge from one or both nipples
- Breast lumps in various locations
- Breast pain that is constant
- If the contour of one or both nipples changes (inverts),
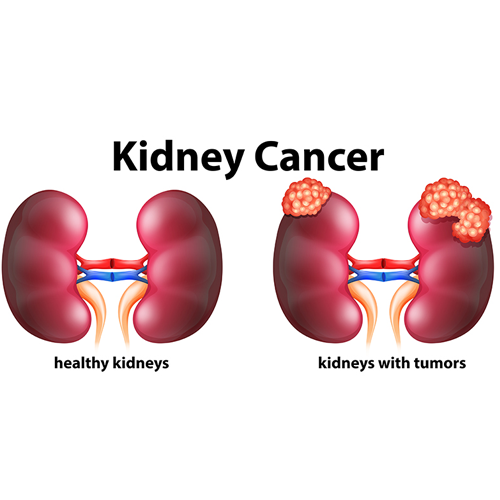
Kidney cancer
Kidney cancer begins in the kidneys, which are two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine and help in blood filtering. As blood flows through the kidneys, waste materials and extra water are collected and converted into urine. In addition, the kidneys create three essential hormones:
- Erythropoietin: This hormone is in charge of the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Renin is a hormone that controls blood pressure.
- Calcitriol: Aids in the absorption of calcium from the diet.
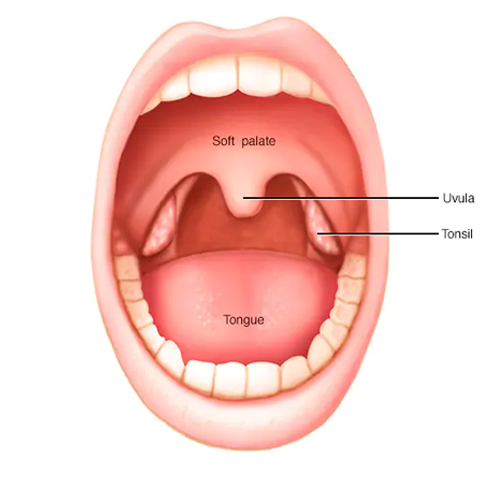
Tonsil cancer
Tonsil cancer is a rare kind of cancer with symptoms that are similar to those of other disorders. It is a kind of head and neck cancer that starts in the oropharynx (the back of your throat). Tonsils are oval-shaped pads located in the back of the mouth that are part of the body’s immune system.
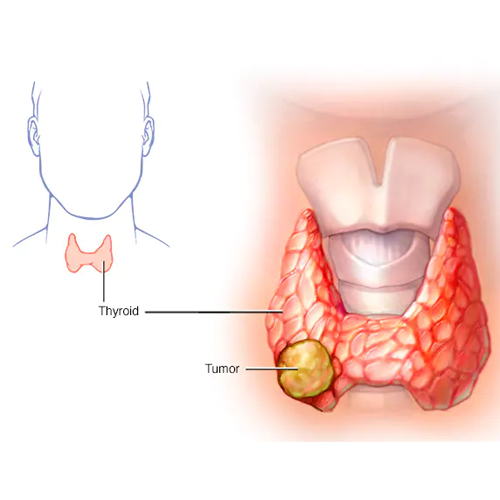
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer develops when thyroid gland cells proliferate excessively, forming tumors that can infiltrate the tissues of the neck, spread to the surrounding lymph nodes, or enter the bloodstream and spread to other regions of the body. Thyroid cancer is classified into four types: papillary, follicular, anaplastic, and medullary.
an uncommon malignancy that affects women 2-3 times more than men.
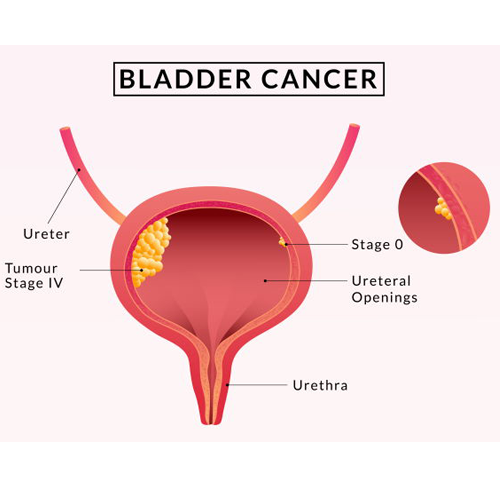
Bladder Cancer
In human bodies, the urinary bladder acts as a storage facility for pee. It allows urine to be stored for a length of time before being released as we pee. Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder lining proliferate abnormally, forming tumors that can infiltrate normal tissues and spread to other regions of the body.
It is the fourth-most prevalent male cancer and the eighth-most common female cancer.
Brain Tumor : Symptoms and Signs of a Brain Tumor
The following signs or symptoms may be present in people with brain tumors: A symptom is anything that can only be recognized and described by the person who is experiencing it, such as exhaustion, nausea, or discomfort. An indicator, such as a fever, rash, or increased pulse, is something that other people can spot and quantify. Together, symptoms and indicators can be used to characterize a medical condition. Sometimes those who have brain tumors don’t exhibit any of the symptoms listed below. Or, a medical disease other than a brain tumor may be the origin of a symptom or a sign.
Both general and particular symptoms of a brain tumor are possible. The tumor’s pressure on various body parts results in a broad spectrum of symptoms.
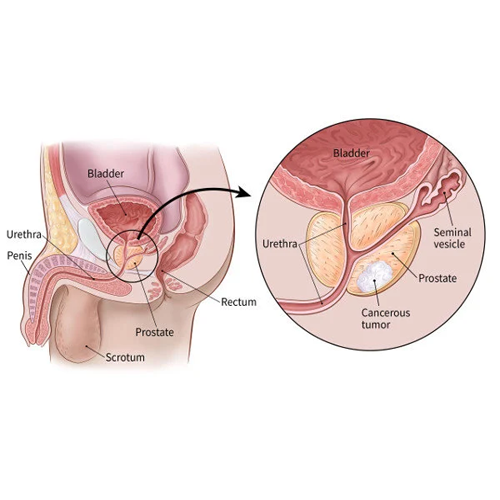
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a kind of cancer that develops there. Males have a little gland called the prostate that resembles a walnut and secretes seminal fluid, which feeds and carries sperm.
One of the most typical forms of cancer is prostate cancer. Numerous prostate cancers have a moderate growth rate and are localized to the prostate gland, where they may not pose a major threat. However, while some prostate cancers are aggressive and spread fast, others are slow-growing and may require little or no therapy.
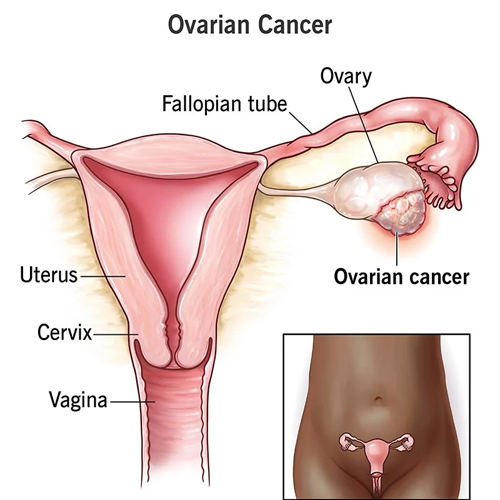
Ovarian cancer
Cancer is a condition in which the body’s aberrant cells grow out of control. Despite subsequently spreading to other body areas, cancer is often named after the area of the body where it first develops.
The term “ovarian cancer” refers to a group of illnesses that start in the ovaries or in nearby organs such as the fallopian tubes and the peritoneum. One ovary is situated on either side of the uterus in the pelvis of women. The ovaries generate female hormones and eggs for sexual reproduction. On either side of the uterus, women have a pair of long, narrow tubes known as the fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are the tubes that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Its lining is called the peritoneum.
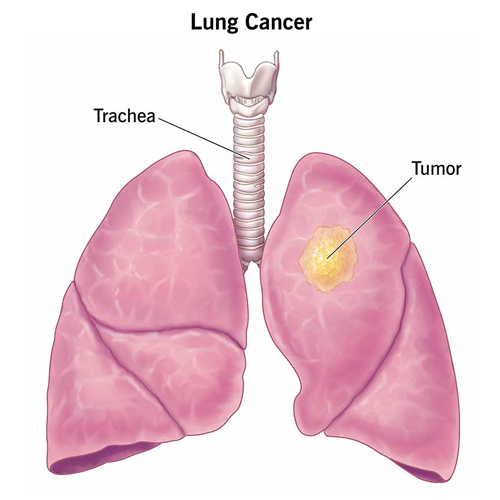
Lung cancer
Cancer is a condition that occurs when the body’s cells grow out of control. Lung cancer is a term used to describe cancer that first appears in the lungs. Lung cancer starts in the lungs and can spread to the lymph nodes or other bodily organs, such as the brain. The lungs may potentially become infected with cancer from other organs. Metastases are the term used to describe the spread of cancer cells from one organ to another.
Small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancers—including adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma—are often categorized into two basic categories. They develop differently and respond to treatment in different ways.
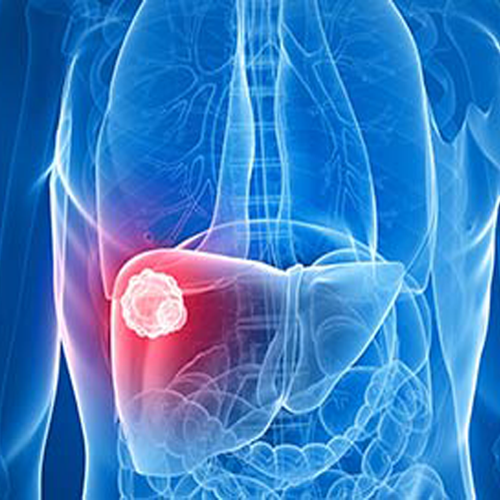
Liver cancer : Liver cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the cells of your liver. The liver is a football-sized organ located in the upper right quadrant of your belly, beneath your diaphragm, and above your stomach.
Several forms of cancer can develop in the liver. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most frequent kind of liver cancer, and it starts in the major type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other kinds of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are significantly less prevalent.
Cancer that spreads to the liver is more prevalent than cancer that originates in the liver cells. Cancer that develops in another part of the body, such as the colon, lung, or breast, and then spreads to the liver is referred to as metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer.